OVERVIEW
“Machinery & Equipment"
The Machinery and Equipment (M&E) Subsector in Malaysia is a significant contributor to the country's economy, accounting for approximately 7% of the country's Gross Domestic Product (GDP). The M&E Subsector includes various industries, such as precision machining, automation and robotics, medical devices, and aerospace.
The Malaysian government has identified the M&E Subsector as one of the main focus areas for growth and expansion, with the Ministry of Investment, Trade and Industry (MITI) indicating that Malaysia has the potential to be a leading regional producer and exporter of M&E. The Malaysian Investment Development Authority (MIDA) has also positioned Malaysia as the destination of choice within the ASEAN region for the M&E Subsector , with forecasted growth of 10.1% per annum between 2018-2027.
Malaysia's conducive business ecosystem for the M&E Subsector has attracted internationally renowned and advanced M&E companies such as SKF, VAT, Oerlikon Balzers, Favelle Favco, Vitrox, SRM, and FMC, among others. Additionally, SMEs account for more than 95% of M&E players in Malaysia.
In terms of contribution to the economy, the M&E Subsector plays a critical role in supporting various industries, including the manufacturing, construction, and transportation sectors. The M&E Subsector also contributes significantly to job creation, with over 100,000 people employed in the sector in 2021.
The M&E Subsector is a vital component of Malaysia's economy, with its growth and expansion playing a crucial role in the country's economic development and global competitiveness.
Productivity Performance
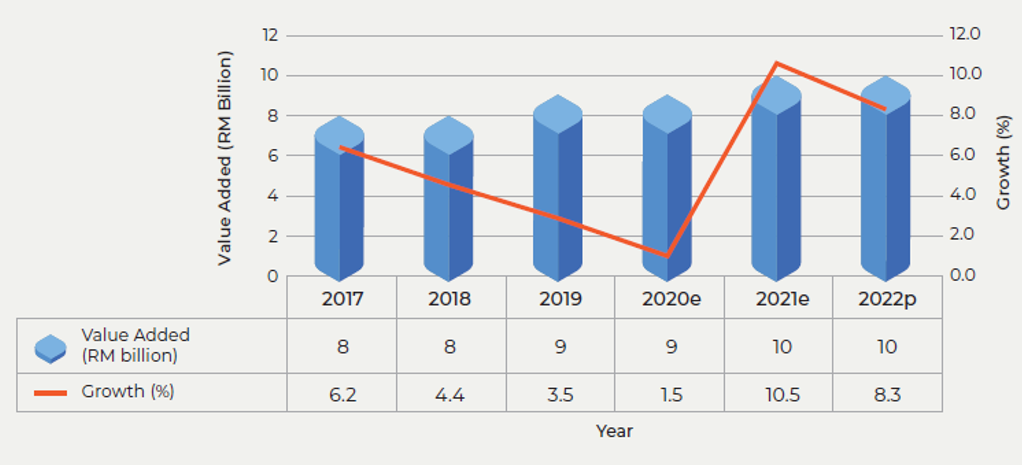
The Machinery and Equipment (M&E) subsector displayed steady growth in value added from 2017 to 2022, with a consistent value of RM 8 billion in 2017 and 2018, followed by incremental increases to RM 9 billion in 2019 and maintaining that level in 2020. Subsequently, the subsector experienced notable expansion, reaching RM 10 billion in 2021 and maintaining this figure in 2022. These value-added figures corresponded to fluctuating growth rates over the same period, starting with a robust 6.2% growth rate in 2017, followed by 4.4% in 2018, and 3.5% in 2019.
The subsector demonstrated resilience with a 1.5% growth rate in 2020. However, the most significant growth occurred in 2021, recording an impressive 10.5% increase, which was followed by a still commendable 8.3% growth rate in 2022. This data underscores the subsector's consistent contribution to economic expansion and its increasing significance within the broader economic landscape.
Challenges
The M&E Subsector faces significant challenges in adapting to the digital age due to a reluctance to change and a preference for traditional business practices. This mindset, coupled with a lack of skilled talent to meet industry demands, hinders productivity growth and progress in the industry. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are particularly affected due to their short-term profit mindset and limited adoption of productivity systems. Additionally, the high cost of digital transformation presents a financial barrier to entry. A gradual transition to digitalization with proper planning and resource distribution is necessary for a successful win-win strategy.
Talent and manpower pose additional challenges to the M&E Subsector with the ongoing Fourth Industrial Revolution constantly challenging business operations. To keep up with the latest technology and perform tasks in new ways, human capital development must be proactive and provide continuous training. Institutions of higher learning and technical vocational education and training (TVET) institutions must be equipped with up-to-date knowledge and technology application to meet industry demands. A sufficient supply of talent from these institutions can alleviate the industry's burden of upskilling or reskilling employees.
INITIATIVES
-
Initiative 1 : Set Up A Partnership Between The Government And Industry Associations To Upskill The Existing Employees
- Develop a framework for upskilling the existing M&E employees
- The Industrial Skill Framework (IndSF)
- Customized Training Programme:
- Visualisation of Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) Programme.
- Digitalisation Transformation – Big Data Analytics Training
- Industry Lean Apprentice Training Course
-
Initiative 2: Set Up A Centre Of Excellence For Skilled Professionals To Share Industry Expertise And Develop New Technologies
- CoE to Enhance Competitiveness and Standard Compliance
- Business Excellence and Productivity Enhancement Programme
- M&E Virtual Advisory Clinic (MEVAC)
- Business Virtual Coordination Programme
- PRODUCTIVITY1010
- Productivity Assessment and Dialogue
- Smart Machinery Programme
-
Initiative 3: Set Up More Product Testing To Ensure Standards Are Met
- Develop a Baseline for Product Testing
- Development of the Repository for M&E Supply Chain
- Development of M&E Cluster Framework
-
Initiative 4: Update To Domestic Product Standards To Be At Part With International Standards And Enforce Compliance
- Review and Update Domestic Product Standard and Enforce Compliance
- Development of National Smart Manufacturing Guidelines
- Streamlining Regulation and Procedure to Reduce the Costs of Doing Business
STAKEHOLDERS
Contact Us
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.
Find Us
Malaysia Productivity Corporation
Lorong Produktiviti Off Jalan Sultan
46200 Petaling Jaya,
Selangor Malaysia
Contact Us
+603 7954 0795
+603 7955 7266
dmo@mpc.gov.my